5205. Parentheses
The pattern is given. It
consists of parentheses and question marks.
Find in how many ways one
can replace the question marks with parentheses to obtain the correct bracket
sequence.
Iput. One line contains the
pattern of length no more than 2000 symbols.
Output. Print the number of ways to
get the correct bracket sequence by modulo 301907.
|
Sampe input |
Sample output |
|
????(? |
2 |
SOLUTION
dynamic programming
Algorithm analysis
Let f(n, k) be the number of correct parentheses
starting at position n, if k open parentheses have already been encountered. Then the
answer to the problem will be the value f(0, 0). Store the value of f(n, k) in dp[n][k].
Let s be the input string. Then:
·
if s[n] = ‘(‘,
then f(n, k) = f(n + 1, k + 1). There will
be k open parentheses before position
n, if there will be k + 1 open parenthesis before position n + 1;
·
if s[n] = ‘)‘,
then f(n, k) = f(n + 1, k – 1) . There
will be k open parentheses before
position n, if there will be k – 1 open parenthesis before position n + 1;
·
if s[n] = ‘?‘,
then at the n-th place one can put both opening and closing parentheses. Therefore f(n, k) = (f(n + 1, k + 1) + f(n + 1, k – 1)) % 301907;
It remains to
write down the conditions for the base case of dynamic:
·
if at some stage becomes k < 0, then the
number of closed brackets turns out to be more than the number of open ones, so
we exit this branch of calculations, return 0;
·
if we have reached the end of the string s0s1 … sn-1 (index numbering starts from zero),
then dp[n][k] = 1 if only k = 0 (when the number of open and closed brackets is the
same). For k > 0, set dp[n][k] = 0.
Example
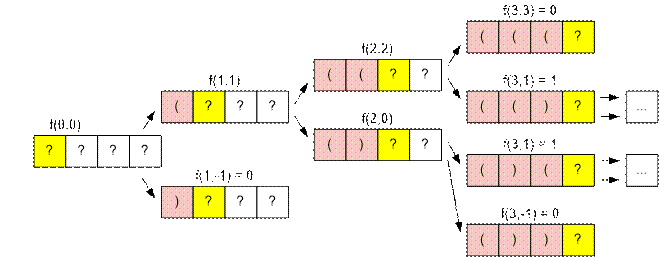
Algorithm realization
Declare the
arrays.
#define MAX 2010
char
s[MAX];
int
dp[MAX][MAX];
int
len;
Implement the function f(n, k).
int
f(int n, int k)
{
if(k < 0) return 0;
if(n == len) return (k == 0);
if(dp[n][k]
!= -1) return dp[n][k];
if(s[n] == '(') return
dp[n][k] = f(n+1, k+1);
if(s[n] == ')') return
dp[n][k] = f(n+1, k-1);
return
dp[n][k] = (f(n+1, k-1) + f(n+1, k+1)) % 301907;
}
The main part of the program. Read the line and print the number of correct bracket sequences.
gets(s);
len = strlen(s);
memset(dp,-1,sizeof(dp));
printf("%d\n",f(0,0));
Java
realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static String s;
static int dp[][];
static int f(int n, int k)
{
if(k < 0) return 0;
if(n == s.length()) return (k == 0) ? 1 : 0;
if(dp[n][k] != -1) return dp[n][k];
if(s.charAt(n) == '(') return dp[n][k] = f(n+1, k+1);
if(s.charAt(n) == ')') return dp[n][k] = f(n+1, k-1);
return dp[n][k] = (f(n+1, k-1) + f(n+1, k+1)) % 301907;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
s = con.next();
int len = s.length();
dp = new int[len ][len ];
for(int i = 0; i < len; i++)
Arrays.fill(dp[i], -1);
System.out.println(f(0,0));
con.close();
}
}